What Is the Molecular Formula of Water? The Simple Answer Behind Earth’s Master Molecule
What Is the Molecular Formula of Water? The Simple Answer Behind Earth’s Master Molecule
Water, the universal solvent and life’s foundation, carries a molecular secret encoded in its formula: H₂O. This unassuming structure—two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom—belies the molecule’s profound physical and chemical significance. With a precise ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, H₂O enables every essential process from cellular hydration to cloud formation.
Understanding its molecular composition is not just a matter of chemistry—it’s key to grasping biology, climate systems, and human civilization itself.
The Core Bonding: Hydrogen and Oxygen in Harmonic Balance
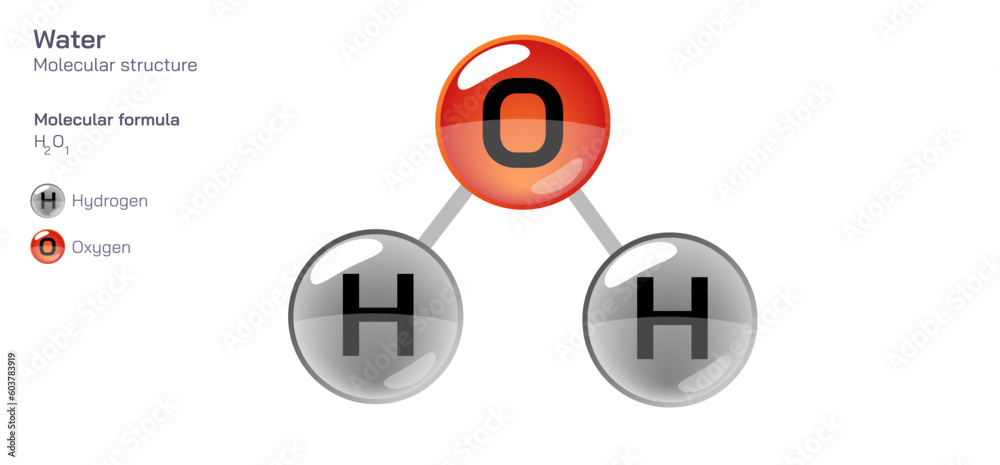
At the heart of water’s identity lies its molecular formula, H₂O. This notation signals two hydrogen atoms tightly bound to one oxygen atom through strong covalent bonds.The oxygen, more electronegative than hydrogen, pulls the shared electrons closer, creating partial negative charges on oxygen and partial positive charges on hydrogen. This polarity is not merely academic—it drives water’s unique behavior. “The polarity of water is the cornerstone of its remarkable properties,” explains Dr.
Elena Martinez, a physical chemist at Stanford University. “It enables hydrogen bonding, a weak but collectively powerful force that shapes water’s structure and function.” Hydrogen bonds arise when the positively charged hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the negatively charged oxygen of a neighboring molecule. These bonds are responsible for water’s high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve a vast range of substances—qualities that sustain life and regulate Earth’s climate.
A Structural Breakdown: Two Hydrogens, One Oxygen—No Adding or Removing
The molecular formula H₂O is deceptively simple but precisely defined. The superscript “2” denotes chemical bonding: two hydrogen atoms sharing electron pairs with a single oxygen atom via sigma bonds. Oxygen contributes six valence electrons—two shared with each hydrogen, completing its octet.Each hydrogen contributes one electron, resulting in a stable eight-electron configuration for oxygen and a duet for hydrogen. This specific stoichiometry prevents water from decomposing into spontaneous components under normal conditions. “The 2:1 ratio defines water’s stoichiometric stability,” notes Dr.
Rajiv Patel, a molecular physicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. “Altering this ratio changes the substance entirely—turning water into hydrogen and oxygen gas upon electrolysis.” No hydrogen, no water. No oxygen, no charge balance critical for polarity.
Beyond Chemistry: How Water’s Formula Powers Life and Planet
The molecular structure of H₂O is not just a scientific curiosity—it directly fuels biological systems and global ecosystems. Water’s ability to act as a universal solvent allows it to transport nutrients, ions, and biochemical signals within cells and organisms. “Without the polarity encoded in H₂O, cellular machinery would collapse,” explains molecular biologist Dr.Lin Mei. “Water’s structure enables it to shuttle molecules across membranes, facilitate enzyme function, and maintain hydration.” In the atmosphere, water molecules form droplets that navigate global weather patterns. The polar nature of H₂O allows for cohesive surface tension, essential for capillary action in plants, enabling water to climb against gravity through narrow xylem vessels.
“From single-celled organisms to human cells, water’s molecular properties underpin every biological process,” Mei adds. On a planetary scale, water’s phase changes—vapor, liquid, and solid—drive the hydrological cycle, regulating temperature, distributing freshwater, and shaping landscapes through erosion and precipitation. “Water moderates Earth’s climate more than any other molecule,” Patel states.
“Its formula is not just chemistry—it’s climate engineering at the molecular level.”
Chemical Reactions and the Limits of H₂O’s Stability
While H₂O is stable under ambient conditions, extreme heat or electrolysis disrupts its bonds. Under normal conditions, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom resist change—but when subjected to high energy, such as in an electrolysis cell, water splits into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂. This reaction, though energetically demanding, defines a fundamental transformation in chemistry and energy technology.“Understanding H₂O’s formula allows us to predict and manipulate its reactivity,” Martinez observes. Whether in cellular respiration, acid rain formation, or industrial hydrogen production, the molecular structure of water remains central. Its stability under ordinary circumstances and reactivity under extreme ones make H₂O unparalleled among molecular compounds.
The Enduring Legacy of H₂O: A Molecular Blueprint for Life
The molecular formula H₂O is more than a chemical notation—it is the foundation of water’s extraordinary ability to sustain life, regulate climate, and enable technological progress. Two hydrogen atoms, bonded to a single oxygen atom, form a molecule that defies simplicity: it is polar, cohesive, dynamic, and indispensable. Science confirms that this precise formula encodes water’s unique properties—its solvent power, thermal stability, and phase behavior—that shape everything from individual cells to global weather systems.No complexity, no transformation, no life-sustaining process is possible without grasping what H₂O actually is. The molecule’s stark elegance—N₂Oous, polar, community-oriented—reflects nature’s precision. In every drop, every vapor trail, and every cloud, the molecular formula H₂O stands as science’s most powerful unlock.



Related Post

Breaking the Cycle: A Short Pidato on the Devastating Reality of Narコ바 Across Generations

Unlocking the Power of Mukadimah Pidato Bahasa: The Voice That Transforms Indonesian Rhetoric

Michael Zegen Movies: The Rising Star Redefining Swiss Cinema with Grit and Gaze

The Free Blessing of the Welkin Moon: A Gateway to Celestial Power in Genshin Impact

