What Is Hochschule? The German Path to Applied Higher Education
What Is Hochschule? The German Path to Applied Higher Education
In the structured landscape of German higher education, Hochschule stands as a distinctive pillar: a specialized institution focused on applied learning, practical training, and direct employability. More than just a vocational college, Hochschule bridges academic rigor with real-world readiness, offering targeted degrees and certifications aligned with Germany’s dual education ethos. This article explores what Hochschul Леagination means in practice, how it differs from universities, and why it plays a vital role in shaping skilled professionals across industries.
The Core Purpose of Hochschule: Praxisnähe Above All
At its foundation, Hochschule is designed to deliver education grounded in practical experience. Unlike traditional universities, which emphasize theoretical research and broad disciplinary study, Hochschulen center their curricula on applied skills and industry-relevant knowledge. > “ Hochschule connects classroom with workplace — it’s not just about knowing theory, but doing it well,” declares Prof.Dr. Lena Weber, education expert at the University of Applied Sciences Berlin. This mission manifests in programs co-developed with local businesses, internships embedded in degree requirements, and faculty with proven professional backgrounds.
Hosting over 400 academic institutions across Germany, Hochschul duent to meet the nation’s demand for skilled tradespeople, technicians, and mid-level managers who can hit the ground running.
Universities vs. Hochschulen: A Defining Divide
While both Hochschulen and universities aim to advance knowledge, their educational philosophies differ sharply.Universities typically offer research-intensive, academically oriented degrees — think law, medicine, and humanities — rooted in critical analysis and theoretical exploration. In contrast, Hochschule programs are purpose-built for immediate job market entry. > “A Hochschule degree is often the golden ticket to professional practice — it’s the bridge between education and employment,” states Dr.
Markus Fischer, vice president of the German Association of Universities of Applied Sciences (dvh). This distinction extends to structure: Hochschulen offer shorter degree cycles—often three to five years—focused on core competencies rather than extensive seminar work. Core subjects include engineering, healthcare, business administration, and information technology, all calibrated to industry standards.
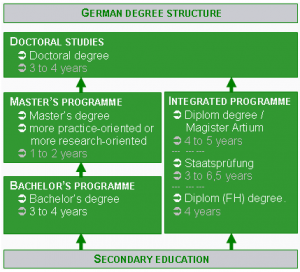
Program Structure and Degrees offered at Hochschule
Hochscheul offerings are meticulously crafted to prepare students for targeted careers. Degrees generally fall into two main categories: Bachelor and Master programs, with many designed around national certification frameworks. - **Bachelor Programs**: Typically lasting three years, these integrate academic theory with hands-on learning through mandatory practicum phases.Engineering students, for example, spend significant time in industrial labs, while health-related programs include clinical training. - **Master Programs**: Available in specialized fields, these advanced degrees deepen professional expertise, often including project-based learning and internships. - **Continuing Education & Short Courses**: Many Hochschulen provide short-term certifications—ranging from coding bootcamps to specialized management workshops—tailored for mid-career professionals seeking targeted upskilling.
Sample curriculum highlights include:
- Automotive Engineering: Combining fluid mechanics theory with diagnostics and repair training in partnership with local mechanics’ cooperatives.
- Healthcare Administration: Blending public health policy analysis with patient service management, preparing for roles in hospitals and public health agencies.
- Business & Digital Marketing: Taught in collaboration with regional SMEs, integrating data analytics with real business strategy.
Employability and Industry Impact
Employers in Germany consistently rank Hochschule graduates as high-value contributors, drawn by the institutions’ focus on competency and readiness. With over 70% of Hochschule students securing jobs immediately after graduation—often within six months—graduates demonstrate strong labor market relevance.Industries from renewable energy to healthcare rely heavily on Hochschul-leissimi. For instance, in the state of Baden-Württemberg, over 60% of entry-level technicians in advanced manufacturing entered via Hochschule programs closely matched to local factory needs. > “Highly practical training reduces onboarding time and ensures candidates already contribute meaningfully,” notes Dr.
Fischer, reinforcing the economic imperative behind Hochschulen’s rise. Moreover, Hochschule supports Germany’s broader innovation ecosystem by fostering applied research. Small-scale R&D initiatives embedded in degree programs frequently lead to patents, process improvements, and regional technological advancement—particularly in digital transformation and sustainability sectors.
Pathways Beyond Hochschule: Opportunities for Further Study
Though Hochschulen offer robust stand-alone degrees, their graduates frequently continue their education at universities. German institutions honor Hochschulabschlüsse for university admission, allowing seamless progression into legal, scientific, or research-oriented fields. Some Hochschulen also maintain dual-degree agreements, enabling students to complete both a practical bachelor’s and lay the groundwork for specialized master’s degrees.This fluidity creates a comprehensive, adaptive educational pipeline suited to Germany’s rapidly evolving economy.
The Cultural and Economic Significance of Hochschule Beyond economics, Hochschule shapes Germany’s social fabric by expanding educational access. Unlike traditional universities—often associated with legacy prestige—Hochschulen are intentionally built for inclusivity, serving first-generation college students, regional workers, and diverse demographic groups.
Their regional campuses decentralize higher education, reducing urban concentration and promoting local development. Economically, this model fuels Germany’s reputation as a global talent hub. By matching educational output precisely to industry demand, Hochschule strengthens workforce resilience, supports lifelong learning, and fosters innovation at the community level.
In Germany’s distributed higher education landscape, Hochschule occupies a vital niche—delivering pragmatic, employable degrees that empower individuals and strengthen national competitiveness. As industries evolve in the digital and green economy era, Hochschule continues to adapt, proving that applied learning is not secondary, but essential.
Hochschulen are more than colleges—they are strategic engines of professional readiness, economic agility, and inclusive growth. By centering practice, fostering real-world skills, and forging seamless ties with industry, they redefine what higher education means in modern Germany and offer a model increasingly studied worldwide.

Related Post

The Snow White Prince: A Grimm Tale of Beauty, Power, and Timeless Relevance

Sara Donchey: Age, Family, and the Journey of a Modern Mother

Nyc Deferred Comp Login: Your Fast & Seamless Access to Manhattan’s Digital Life

What Language Did Vikings Speak? The True Tongue of the Norse Raiders

