Unlocking Molecular Secrets: How Ether Infrared Spectroscopy Revolutionizes Chemical Analysis
Unlocking Molecular Secrets: How Ether Infrared Spectroscopy Revolutionizes Chemical Analysis
Ether infrared spectroscopy stands at the forefront of modern analytical chemistry, offering a precise, non-destructive means to decode molecular structures through vibrational fingerprinting. By measuring how chemical bonds absorb infrared light, this powerful technique reveals detailed information about ether functional groups and their surrounding environments with remarkable accuracy. From pharmaceutical development to forensic science and environmental monitoring, the versatility and sensitivity of ether IR spectroscopy make it an indispensable tool in laboratories worldwide.
Understanding its mechanisms and expanding applications offers fresh insight into how cutting-edge science continues to shape research and industry.
The Science Behind Ether Infrared Spectroscopy: Probing Molecular Vibrations
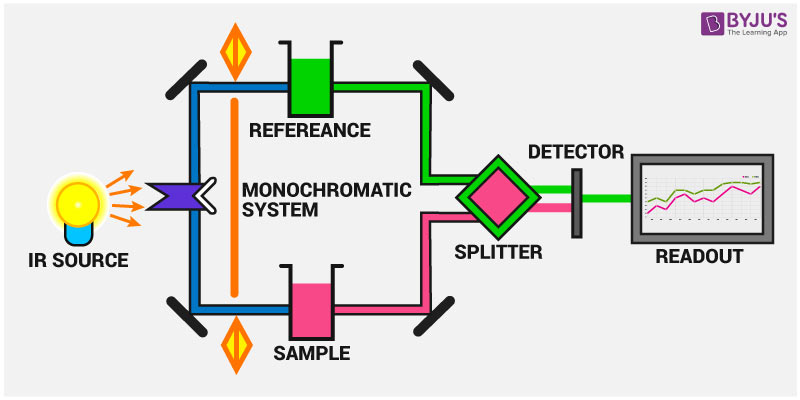
At the core of ether infrared spectroscopy is the principle that molecules absorb infrared radiation at specific frequencies corresponding to the vibrational modes of their chemical bonds. For ethers—organic compounds featuring an oxygen atom linked to two carbon groups—this absorption pattern is uniquely informative. The characteristic C–O–C bending and C–O stretching vibrations typically appear in the 900–1300 cm⁻¹ region, producing a distinct spectral signature that distinguishes ethers from alcohols, esters, or ketones.
“This isn’t just about identifying a functional group—it’s about seeing how bonds behave in real molecular environments,” explains Dr. Elena Vasiliev, a spectroscopist at the Advanced Materials Lab. “Infrared spectroscopy captures subtle shifts caused by hydrogen bonding, solvent effects, or even polymorphic forms, enabling chemists to infer structural details beyond simple connectivity.”
In ether structures, the C–O bond’s vibrational frequency is especially sensitive.
Short, strong C–O stretches around 1100 cm⁻¹ confirm the presence of an ether linkage, while adjacent absorptions—such as the C–O–C asymmetric stretch near 1050 cm⁻¹—provide context about molecular symmetry and conformational stability. When solvents or impurities interact with ethers, shifts and broadening of peaks appear, giving clues about dynamic interactions crucial in formulation science.
Key Applications: From Drug Discovery to Environmental Monitoring
Ether infrared spectroscopy drives innovation across multiple domains, beginning with pharmaceutical research. In the development of ether-containing drugs like propofol—a widely used anesthetic—the technique confirms structural integrity and purity at every stage.
“IR spectroscopy allows us to monitor reaction progress in real time, ensuring the formation of the correct molecular architecture without damaging delicate compounds,” notes Dr. Marcus Lin, a medicinal chemist at a leading biotech firm.
Beyond healthcare, the method plays a vital role in forensic analysis, where identifying controlled substances or trace evidence demands unmatched specificity. Ether IR spectra help differentiate designer drugs, such as ethylmorphine or synthetic cannabinoids, by revealing unique vibrational shifts tied to their ether moieties.
This capability supports law enforcement and forensic labs in tracking and classifying substances beyond traditional methods.
Environmental scientists rely on ether spectroscopy to detect and quantify trace organic pollutants. In water quality monitoring, for instance, distinguishing ether-based industrial solvents from natural organic matter helps assess contamination sources and guide remediation. Air quality studies similarly utilize IR spectroscopy to track volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in urban and industrial settings, where ethers may serve as stable tracers or pollutants.
How Ether Infrared Spectroscopy Delivers Precision and Speed
One of the standout strengths of ether infrared spectroscopy is its speed and minimal sample preparation.
Unlike chromatographic techniques requiring separation, IR measurement typically takes seconds per sample under transmission mode—enabling high-throughput analysis. Advances in FTIR (Fourier-transform infrared) technology further boost resolution and sensitivity, allowing detection of minute concentrations even in complex matrices.
Portable IR spectrometers have extended the technology beyond laboratory walls.
Field-deployable devices now support rapid on-site analysis in forensic investigations, pipeline integrity checks, and real-time environmental monitoring. “These sensors bring analytical accuracy into the hands of first responders and field technicians,” says Dr.



Related Post

Is I Am Security Free On Oculus Quest? The Detailed Breakdown
NoahKahanMarried: The Quiet Evolution of a Songwriting Icon at the Peak of His Personal Journey

What Is Time Brazil? The American Time Zone That Shapes a Vast Nation
Unlocking Market Dominance: The Role of Commercial Real Estate Analysis and Strategic Investments in PDF Insights

