Unlocking Critical Insights: The Vital Role of Iv Peripheral Sites in Modern Medicine
Unlocking Critical Insights: The Vital Role of Iv Peripheral Sites in Modern Medicine
In the evolving landscape of clinical medicine, Iv Peripheral Sites have emerged as indispensable access points for efficient patient care, particularly in rapid infusion settings. These peripheral sites—normally located on the extremities, most commonly the antecubital fossa in the elbow or radial veins in the wrist—serve as primary entry points for intravenous therapy, offering clinicians swift, reliable routes for administering fluids, medications, and emergency drugs. Their strategic placement and accessibility make them central to both emergency response and ongoing treatment in hospitals and clinics.
As healthcare increasingly emphasizes speed, safety, and accessibility, a deeper understanding of Iv Peripheral Sites is essential for optimizing patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
At their core, Iv Peripheral Sites are small-diameter, easily accessible peripheral veins ideally suited for short- to medium-duration intravenous therapy. Unlike central venous access devices, which require more complex placement and pose higher risks of complications such as infection or thrombosis, peripheral sites offer a minimally invasive alternative with rapid insertion and straightforward management.
According to interventional radiologists and emergency physicians, "The antecubital region remains the workhorse for most IV access due to its consistent vein size, low complication rate, and ease of recognition—even in challenged patients." This reliability supports their widespread use in emergency departments, outpatient infusion centers, and even ambulatory care settings.
Anatomy and Clinical Suitability
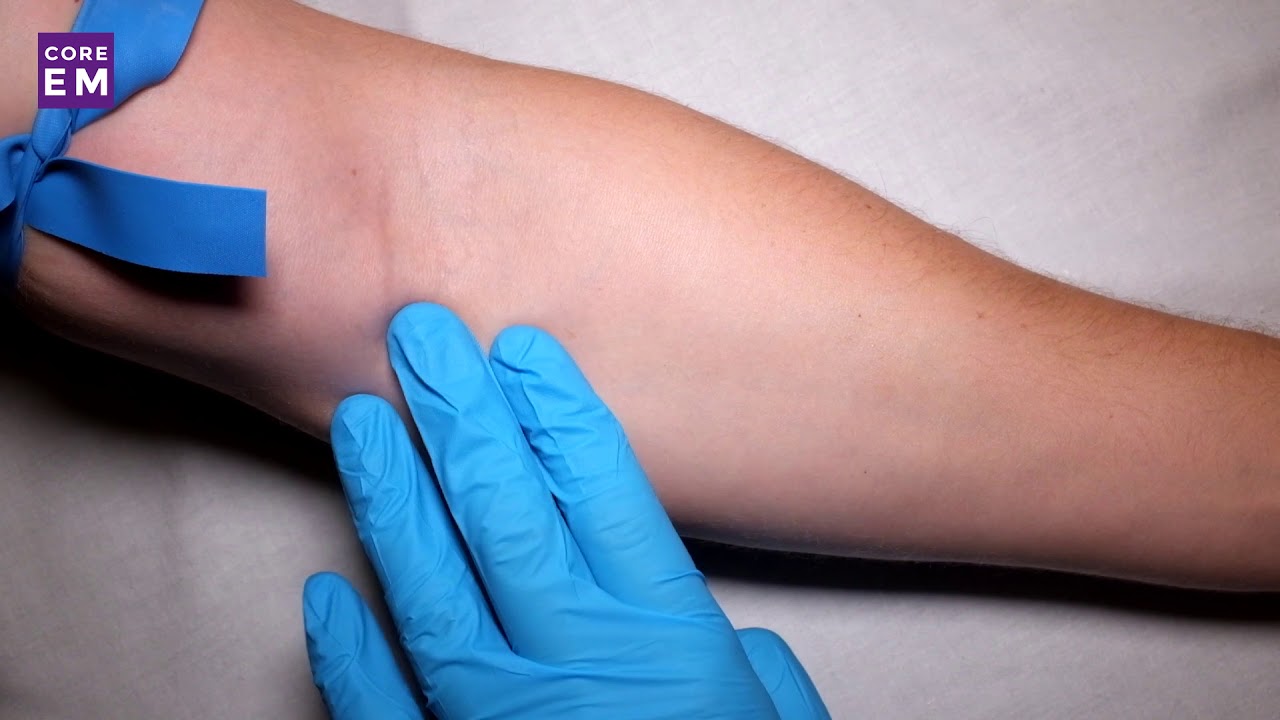
The selection of an ideal Iv Peripheral Site hinges on precise anatomical knowledge and an understanding of vascular dynamics. Major superficial veins in the upper limbs—such as the cephalic, basilic, and median cubital veins—serve as the most common sites.These veins, typically 1.5 to 3 millimeters in diameter, provide sufficient flow for most clinical therapies without requiring invasive insertion techniques. The antecubital fossa, located just below the elbow, is particularly favored because of its superficial depth and the gentle angle of vein entry, reducing needle bend and tissue trauma. In contrast, deeper peripheral sites like the radial vein may be used in specific scenarios but carry higher risks due to anatomical complexity.
Successful cannulation depends not only on vein size but also on patient-specific factors including vein patency, skin condition, and hemodynamic status. Pediatric patients, elderly individuals with fragile vasculature, and critically ill patients all present unique challenges. "Real-world success for peripheral IV access often depends on clinician palpation skills—being able to feel a quiet but visible vein and avoid Taletta’s area, where vessels are narrow and prone to collapse," notes a leading vascular access specialist.
Advanced training emphasizes systematic evaluation: visual inspection, gentle palpation, and adaptive needle insertion angles tailored to vein behavior under pressure.
Operational Advantages in Healthcare Systems
Beyond anatomical suitability, Iv Peripheral Sites deliver tangible operational benefits that transform clinical workflows. Rapid cannulation improves patient throughput in emergency departments, where timely administration of fluids, antibiotics, or thrombolytics can be lifesaving.In outpatient settings, reliable peripheral access enables safe long-term IV therapy—such as chemotherapy, anticoagulants, or total parenteral nutrition—without the need for central line insertion, thereby reducing infection risks and hospital stays.
Healthcare institutions have increasingly adopted standardized protocols to optimize peripheral IV use. For instance, many hospitals implement "point-of-care" venipuncture programs where trained staff perform rapid assessments and insert peripheral devices within minutes, decreasing reliance on central lines routed to specialized teams.
Data indicates that mucosavputkiftsich peripheral IV access reduces knockout times by up to 40% during emergencies and decreases prolonged catheter use linked to bloodstream infections. "In high-volume units, the ability to place a peripheral line quickly avoids bottlenecks, ensuring patients receive care when it matters most," states a hospital infusion nurse with over a decade of frontline experience.
Risk Management and Best Practices
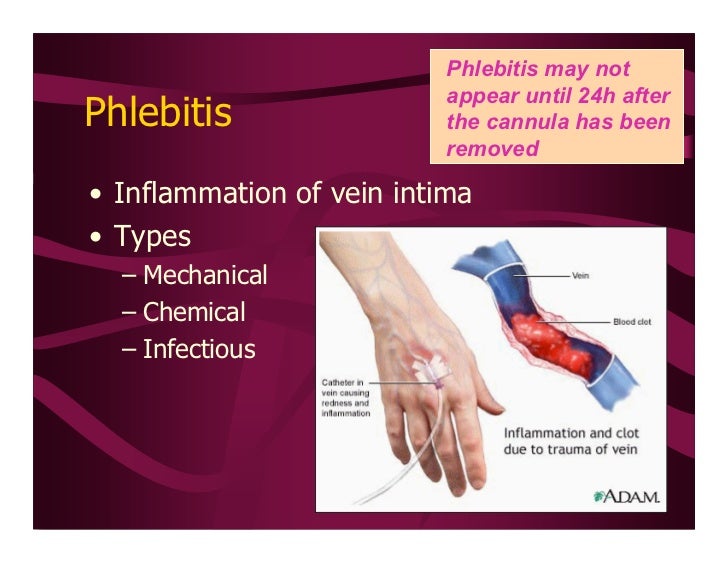
While Iv Peripheral Sites offer significant advantages, their use demands strict adherence to infection control and site maintenance protocols.Despite lower complication rates compared to central lines, improper technique or neglect of aftercare can lead to phlebitis, infiltration, or infection. The warm-apply-dress technique—mittens thermotherapy followed by sterile dressing—has become a gold standard for minimizing inflammation and preserving vessel integrity. Regular site monitoring and prompt rescue to alternative sites when needed prevent complications and sustain effective therapy.
Key best practices include: - Using aseptic technique consistently - Limiting infusion duration to prevent vein damage - Rotating access sites when multiple veins are available - Educating staff on early signs of complications like redness or swelling - Maintaining detailed documentation for continuity of care 综上,Iv Peripheral Sites represent a cornerstone of modern intravenous therapy, balancing clinical effectiveness with logistical practicality. Their strategic deployment in emergency, outpatient, and critical care settings underscores their role in enhancing both patient safety and system efficiency. As clinical protocols evolve and technology advances—such as improved vascular imaging and needle design—the integration of IV Peripheral Sites continues to grow, solidifying their position as essential assets in the pursuit of optimal patient-centered care.


Related Post

Cristiano Ronaldo’s Stature: More Than Just a Physical Edge in the Game

Watch the Full Hindi Blockbuster: Pushpa: The Rise Drops – The Story of a Rural Warrior

San Antonio Time: How the Cactus City Stays Ahead Across Central Time

Unveiling the Origins of Psalm 23: A Timeless Prayer Rooted in Ancient Tradition