Unlock Remote Access & Image HTML: The Hidden Power of Camera Live Feeds
Unlock Remote Access & Image HTML: The Hidden Power of Camera Live Feeds
Animal with a camera rolling, staff members reviewing live feeds from different city parks, and security operators monitoring public spaces—this seamless blend of technology reveals how modern surveillance and access control are transforming public safety and visitor engagement. Behind the flashing monitors and instant feeds lies a sophisticated ecosystem powered by camera live feeds that enable remote guest access and precise HTML-driven image management. Far from being just a visual update, these systems unlock real-time collaboration, secure authentication, and dynamic content delivery—secrets encoded in both software logic and web architecture.
Understanding their inner workings reveals not just operational advantages, but profound implications for privacy, efficiency, and innovation in monitored environments.
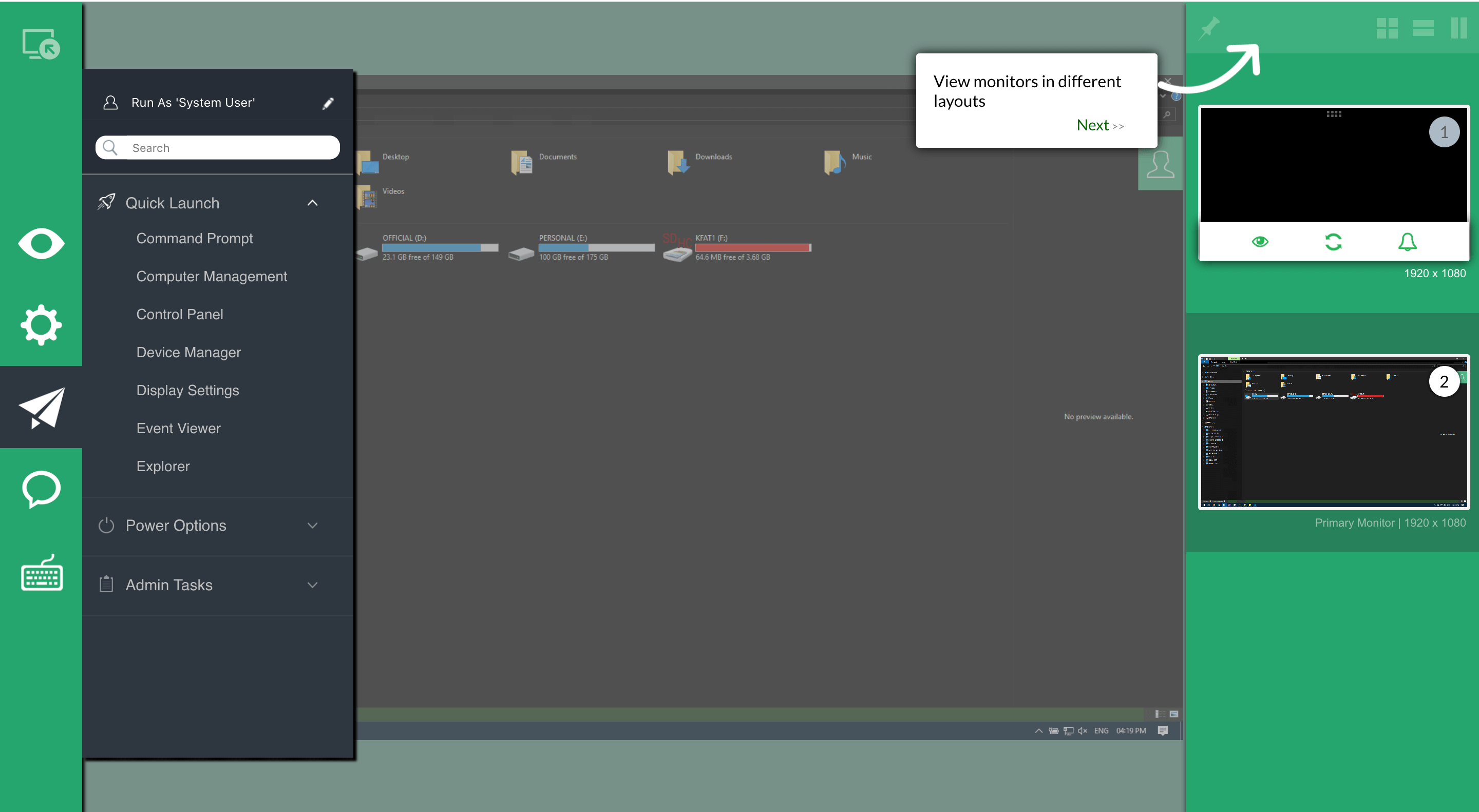
At the core of modern camera live feed systems is guest access management—both physical and digital. Access is no longer limited to secured rooms or on-site personnel; instead, verified visitors, remote technicians, and authorized staff gain controlled entry to live feeds through authenticated portals.
This access is governed by robust security protocols, often leveraging HTTPS encryption, role-based permissions, and time-limited session tokens. As one security consultant notes, “True guest access isn’t about giving open remote control—it’s about precision: who sees what, when, and under what conditions.” On-premise servers and cloud-based platforms work in tandem to ensure that guest views remain synchronized, delayed or restricted as needed, preventing unauthorized viewing while enabling collaboration across locations. Whether monitoring from corporate headquarters or coordinating emergency responders across city zones, the ability to selectively grant live camera access has redefined operational agility.
The HTML Engine Behind Secure Image Delivery
HTML—often seen merely as a structural web language—plays a foundational role in how live camera feeds are rendered, accessed, and manipulated in real time. Behind every clickable thumbnail, interactive image grid, or dynamic stream overlay lies carefully crafted HTML that balances speed, security, and interactivity. Developers embed AV and WebRTC protocols directly into HTML5 frameworks, enabling live feeds to display without plugin dependencies while embedding strong encryption via HTTPS.Crucially, image access and display rules are encoded within HTML metatags and JavaScript event handlers, defining permissions at a granular level.
Supporting secure image delivery requires more than static web files. Developers implement Content Security Policies (CSP) to block malicious script injections, while CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) configurations ensure only trusted domains access feed data.
Preview tiles and thumbnail galleries are dynamically generated using HTML snippets that call secure API endpoints, ensuring guest viewers capture only authorized previews, not raw high-resolution streams. As a front-end engineer explains, “The HTML code isn’t just visual—it’s a gatekeeper. Every image element carries metadata that enforces access policies, session checks, and device trust levels.” This integration of security into markup transforms HTML from passive layout into an active protector of sensitive visual data.
Practical Use Cases: From Smart Cities to Corporate Audits
The application of guest access and HTML-secured image feeds reaches across public and private sectors. In urban settings, city operators use live camera feeds accessed by maintenance crews and emergency teams—each viewer granted real-time image data through authenticated HTML portals resistant to spoofing. For instance, installing a camera at a public fountain for crowd monitoring becomes unlockable only to assigned staff via a secure web portal, where images appear in interactive dashboards with markers, location tags, and timestamp overlays—all generated dynamically with HTML and JavaScript.In corporate environments, Retrieved Site Analytics (RSA) teams use live feeds to audit remote visitors during facility access, combining video verification with access logs stored via secure HTML-based interfaces. Similarly, event security personnel in stadiums or conventions exploit guest portal integrations, where authorized observers preview live footage through browser-based dashboards—no app download required. Each use case leverages HTML’s ability to embed encrypted, permissioned image streams directly into responsive web pages, merging instant visibility with strict control.
Beyond delivery, HTML supports advanced features such as zone tagging, frame timestamping, and guest session expiration—all controlled through logic embedded in HTML code. For example, a live feed URL might include a guest token appended via `?guest=abc123&access=2h`, enforced server-side by validating the token against a secure API before granting access. Such integration exemplifies how image HTML secrets function as both user interface and access mechanism, reducing attack surfaces while



Related Post
The Ultimate Full-Screen Instagram Story Repost: Easy Guide to Mastering Visual Storytelling
Unlocking Ll.A: The Next Evolution in Language Modeling Power

What Century Are We In? Navigating the Age of Digital Transformation and Existential Shifts
.jpg?itok=GL4841nH)
Jellybeanbrains: The Latest Leaks That Shook the Internet to Its Core
![The Revolutionary Power of [50 Bmg]: Transforming Health, Performance, and Everyday Energy](https://getitnow.ai/storage/blog/658436079.jpg)
