Understanding Atpl Brain Disease Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Atypical Autoimmune Encephalopathy (APE), often colloquially referred to as Atpl Brain Disease, represents a rare but serious neurological condition rooted in immune system dysfunction targeting brain tissue — a complex disorder that challenges both diagnosis and treatment. Unlike more common neurological disorders, APE arises when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks neural proteins, leading to inflammation, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms early, and identifying effective treatment strategies are critical for reducing long-term damage and improving patient outcomes.
This article delves into the intricate science behind this condition, shedding light on its origins, manifesting signs, and evolving therapeutic approaches.
Unraveling the Causes: How Autoimmunity Triggers Brain Dysfunction
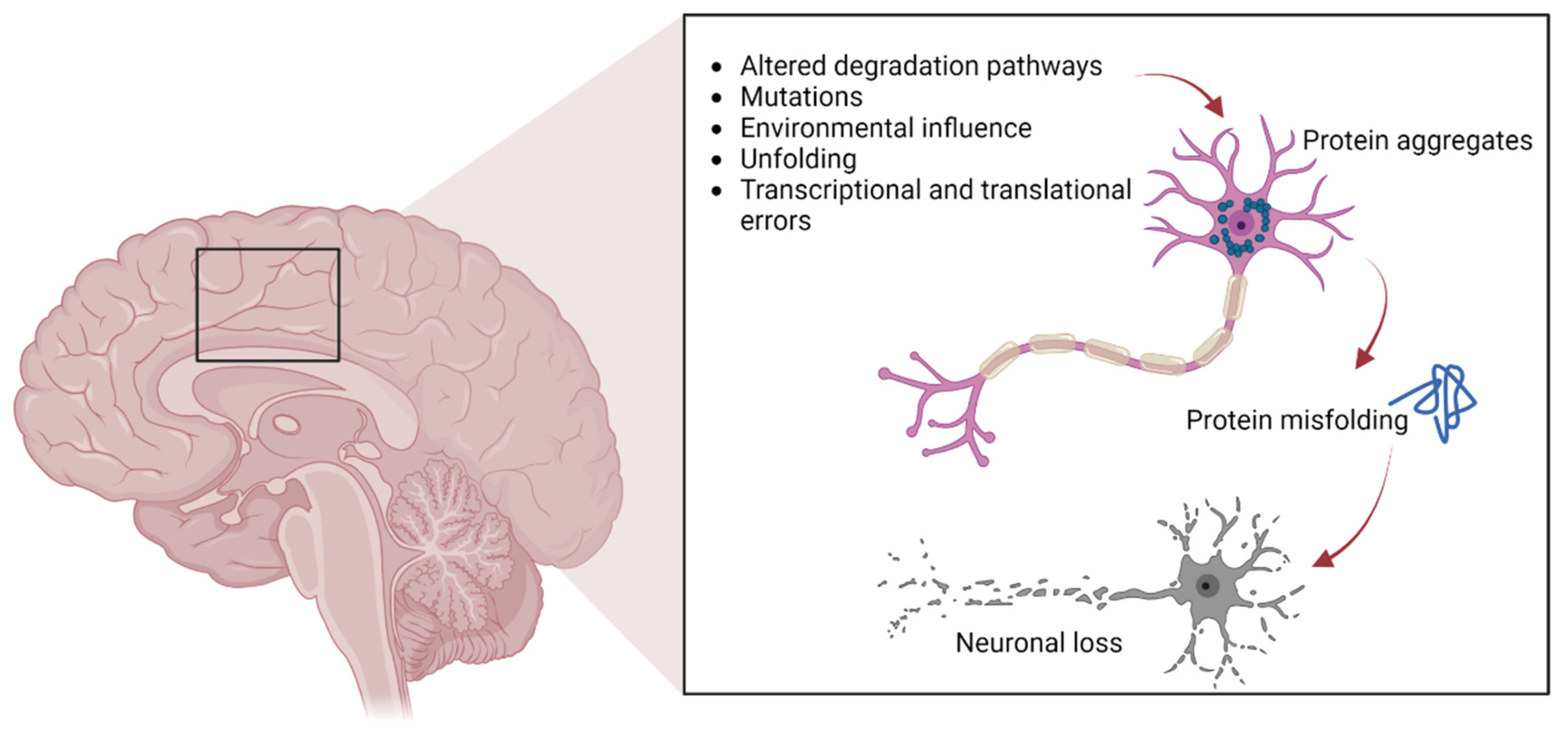
Atypical Autoimmune Encephalopathy arises from autoimmune mechanisms, where the body’s own immune defenses mistakenly target brain-associated proteins. Though the exact triggers remain partially elusive, research identifies several contributing factors. The most prominent are paraneoplastic syndromes — conditions where tumors prompt immune responses that cross-react with neural tissues — and post-infectious or post-vaccination autoimmunity, where prior exposure to pathogens or immunization activates aberrant immune pathways targeting brain antigens.Common neural antigens targeted include NMDA receptors, LGI1 (ligand-gated ion channel protein 1), CASPR2 (Contactماذا.ru), and others. When these targets are assaulted, immune cells infiltrate brain parenchyma, leading to inflammation and neuronal dysfunction. "Some patients develop APE following a viral infection or tumor-related immune activation, illustrating how close the immune system is to self-targeting when regulation fails," explains Dr.
Elena Martinez, a neurologist specializing in neuroautoimmune disorders. Genetic predisposition also plays a role, with certain HLA gene variants increasing susceptibility, suggesting a complex interplay between inherited risk and environmental exposure. While exact mechanisms are still under investigation, advances in immunotherapy and biomarker discovery continue to clarify how autoantibodies disrupt synaptic function, impairing memory, movement, and behavior.
Recognizing the Symptoms: From Subtle Change to Severe Decline
Symptoms of Atpl Brain Disease often mimic other neurological or psychiatric conditions, making early detection difficult but critical. The disorder presents with a spectrum of cognitive, emotional, motor, and autonomic disturbances, frequently evolving over days or weeks. Recognizing these signs promptly can significantly impact prognosis.Cognitive impairment is a hallmark: patients may experience rapid memory loss, disorientation, and difficulty concentrating — symptoms sometimes mistaken for dementia or delirium. Emotional and behavioral changes are equally prominent, including unpredictable mood swings, anxiety, depression, or even psychotic features without clear cause. Motor symptoms frequently involve movement disorders such as myoclonus (involuntary muscle jerks), ataxia (loss of coordination), and seizures.
Autonomic dysfunction — irregular heart rate, blood pressure fluctuations, and temperature instability — further complicates clinical evaluation. A key diagnostic challenge lies in symptom overlap with other conditions like sepsis, encephalitis, or autoimmune encephalitis. Patients often present with confusing or fluctuating neurology, requiring multidisciplinary assessment involving neurology, immunology, and infectious disease specialists.
"Patients may appeararded with fluctuating confusion, sudden mood shifts, or unexplained motor symptoms — all red flags only fully understood through comprehensive autoimmune screening," notes Dr. Samuel Chen, chief of neuroimmunology at a leading medical center. Timely identification relies on targeted antibody testing, brain MRI showing characteristic inflammation patterns, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis revealing elevated inflammatory markers and specific autoantibodies.
Early symptom awareness empowers clinicians to initiate prompt immunomodulatory therapy.
Breakthrough Treatments: Managing Autoimmune Encephalopathy
Effective treatment of Atpl Brain Disease hinges on suppressing the abnormal immune response and mitigating ongoing neuronal damage. The cornerstone of management is immunotherapy, tailored to the specific autoantibody profile and disease severity.First-line therapies typically involve high-dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), or plasma exchange (plasmapheresis), which rapidly reduce autoantibody levels and immune-mediated inflammation. For refractory cases, more aggressive approaches such as rituximab — a monoclonal antibody targeting B cells responsible for autoantibody production — have shown significant benefit. "In many patients, rituximab brings a measurable reversal of neurological deficits when administered early, highlighting the importance of timely intervention," says Dr.
Chen. In both acute and maintenance phases, long-term immunosuppressive regimens, including azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil, help prevent relapse and secure remission. Adjunctive therapies address symptom control: antiepileptic drugs manage seizures, neuroprotective agents reduce excitotoxicity, and psychiatric medications stabilize emotional and behavioral symptoms.
Rehabilitation — including cognitive therapy, physical therapy, and speech training — plays a crucial role in restoring function lost during acute phases. Emerging research into B-cell depletion, convalescent plasma, and novel biologic agents offers hope for improved outcomes. Clinical trials are investigating personalized immune modulation strategies, aiming to balance efficacy with minimal long-term side effects.
While Atpl Brain Disease remains a complex and evolving challenge, integrated care combining precise immunomodulation, symptom management, and rehabilitation continues to transform patient trajectories. As scientific understanding deepens, earlier diagnosis and more targeted therapies promise not only to reduce disability but to reclaim neurological health for those affected.
![Atpl Brain Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment | [Overview]](https://scitechdaily.com/images/Brain-Disease-Scan-Neurological-Disorder-Art-Concept.jpg)


Related Post

Copa América De Voley 2025: The Tournament Redefining South American Volleyball

Vivo 2 Via: The Game-Changing Smartphone That Redefines Android Experience

Sibi Blažić: Redefining Entrepreneurship, Innovation, and Digital Influence in the Balkans

Guatemala vs Panama: Predicted Lineups and Team News Shape a High-Stakes Clash in the Central American Cup

