SFMI Medical Term: Unlocking the Power of Stereotactic Frontal Cortical Thermotherapy in Neurological Care
SFMI Medical Term: Unlocking the Power of Stereotactic Frontal Cortical Thermotherapy in Neurological Care
When it comes to advancing precision medicine in neurosurgery, few innovations are as transformative as stereotactic frontal cortical thermotherapy (SFMI)—a medical term describing a minimally invasive thermal ablation technique that targets specific brain regions with extreme accuracy. Used primarily to treat refractory epilepsy, essential tremor, and certain psychiatric disorders, SFMI leverages sophisticated imaging and thermal mapping to deliver controlled heat ≥60°C to pathological neural tissue while sparing surrounding healthy structures. This breakthrough procedure exemplifies how targeted neuromodulation is reshaping neurological treatment.
What defines SFMI in modern neurology? At its core, SFMI integrates stereotactic guidance—a three-dimensional coordinate system for locating brain targets—with thermotherapy devices that generate localized heat via radiofrequency or microwave energy. Unlike conventional ablation methods requiring extensive open surgery, SFMI operates through small burr holes (2–4 mm), drastically reducing recovery time and risks. “SFMI allows us to precisely deliver therapeutic energy to frontal brain circuits involved in seizures or tremors—without the need for full thalamotomy or cortical resection,” explains Dr.
Elena Marquez, neurosurgeon and pioneer in stereotactic thermal techniques. “This precision preserves critical cognitive functions while effectively disrupting pathological neural networks.”
SFMI’s foundation rests on precise anatomical targeting guided by MRI fusion imaging. Before treatment, high-resolution MRI scans are registered with a stereotactic framework, creating a detailed 3D map of the frontal cortex.
Clinicians then plan energy delivery based on the patient’s unique neural architecture, applying thermal energy in carefully calibrated pulses and durations. Temperature sensors monitor real-time changes, ensuring the target reaches optimal therapeutic thresholds while avoiding thresholds that damage adjacent tissue. “Controlling these heat dynamics at a millimeter scale is what distinguishes SFMI from earlier thermal therapies,” notes Dr.
Rajiv Nair, a neuro-interventional specialist. “We’re no longer speculative—we’re achieving reproducible outcomes grounded in biophysical modeling and clinical validation.”
Clinical applications of SFMI span several disabling neurological conditions. In epilepsy—especially mesial temporal lobe epilepsy resistant to medication—SFMI targets the epileptogenic zone within the frontal lobe, often the anterior inferior limb of the corpus callosum.
Studies report seizure reduction in over 70% of patients at 12-month follow-up, with medication withdrawal possible in a significant subset. Similarly, in essential tremor, stimulating and ablating hyperactive nodes in the thalamocortical loop leads to long-term tremor control comparable to deep brain stimulation but with lower procedural morbidity. For psychiatric conditions like treatment-resistant depression, emerging research explores SFMI’s potential in modulating dorsolateral prefrontal circuits via controlled thermal modulation—a frontier still under rigorous clinical investigation.
The safety profile of SFMI represents a major advancement over older modalities. Traditional radiofrequency ablation or laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) require craniotomy and carry higher risks of infection, hemorrhage, or neurological deficits. SFMI’s minimally invasive approach slashes complications to less than 3% when performed by experienced operators, as reported in multicenter trials.
“Patient safety isn’t an afterthought—it’s woven into every phase of SFMI protocol,” emphasizes Dr. Marquez. “From patient selection using advanced neuroimaging to real-time temperature feedback, we prioritize minimizing risk without sacrificing efficacy.”
The technology behind SFMI continues to evolve rapidly.
Innovations such as robotic-assisted delivery systems promise even finer control, while machine learning algorithms refine thermal modeling based on individual neuroanatomy and thermal response patterns. Portable or hybrid devices may soon expand accessibility beyond specialized centers, bringing precision therapy to community hospitals and regional clinics. “The future of SFMI isn’t just about treating disease—it’s about redefining normal brain function,” says Dr.
Nair. “By enabling reversible and adjustable targeted neuromodulation, we’re opening doors to personalized neurological care that adapts to the patient’s unique biology.”
Despite its promise, SFMI remains underutilized, partly due to limited awareness and training. The procedure requires multidisciplinary collaboration—neurosurgeons, neurologists, radiologists, and medical physicists—alongside fluency in advanced imaging physics.
Professional societies, including the International Society for Stereotactic and Functional Neuroscience (ISSFN), are working to standardize guidelines, expand training networks, and promote evidence-based adoption. With ongoing clinical trials documenting long-term outcomes, SFMI is transitioning from experimental novelty to established therapeutic option.
As research deepens understanding of thermal dynamics in neural tissue, SFMI is poised to become a cornerstone of minimally invasive neurotherapeutics.
Its fusion of precision, safety, and efficacy exemplifies the next generation of brain-targeted interventions—where science meets compassion in the pursuit of healing. For patients burdened by conditions once deemed untreatable, SFMI offers not just relief, but renewed hope, delivered one exact degree of heat at a time.



Related Post
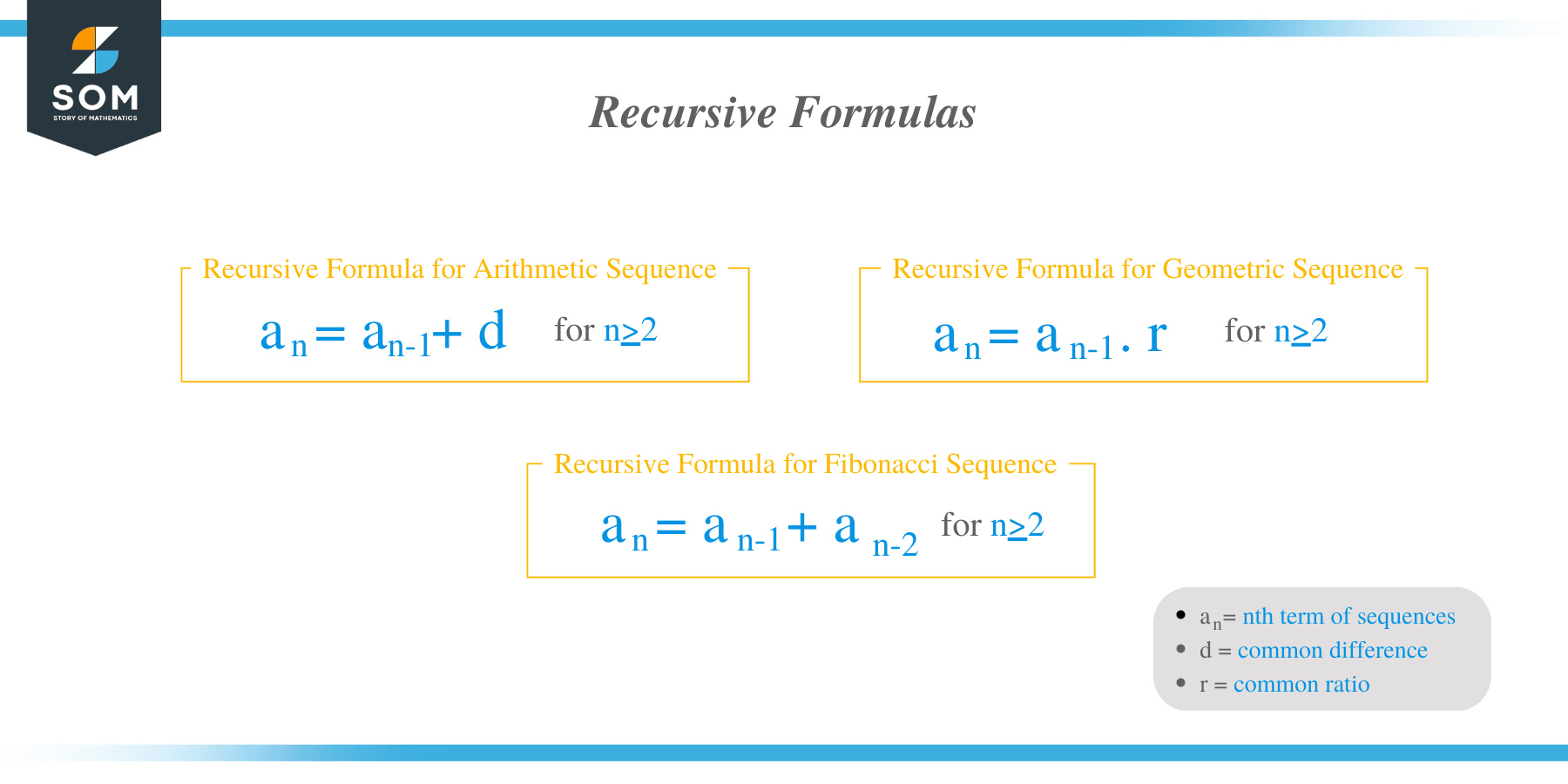
Decode Mc005: The Recursive Rule Behind the Mc005 Sequence Jpg

Hi Five Vs High Five: The Debate That’s Ranging Through Social Media and Sports Culture

Return To The Blue Lagoon Trailer Dive In: A Deep Dive into the Mythical Ocean Escape

Valorant Lunar New Year Bundles: Celebrate In Style – Deck Up for Festival Flair

