Pacific Standard Time What Time Is It In The Usa
Pacific Standard Time What Time Is It In The USA reveals a dynamic, continent-spanning concept shaped by geography, federal policy, and cultural rhythm. With the U.S. spanning nine time zones across the Americas, timekeeping reflects both precision and regional diversity.
Pacific Standard Time (PST), observed in the westernmost part of the U.S., serves as a benchmark for millions—from tech innovators in San Francisco to farmers in rural California. This article unpacks the technical, social, and geographic layers behind how time is measured and perceived across the country, focusing squarely on Pacific Standard Time as a key reference point.
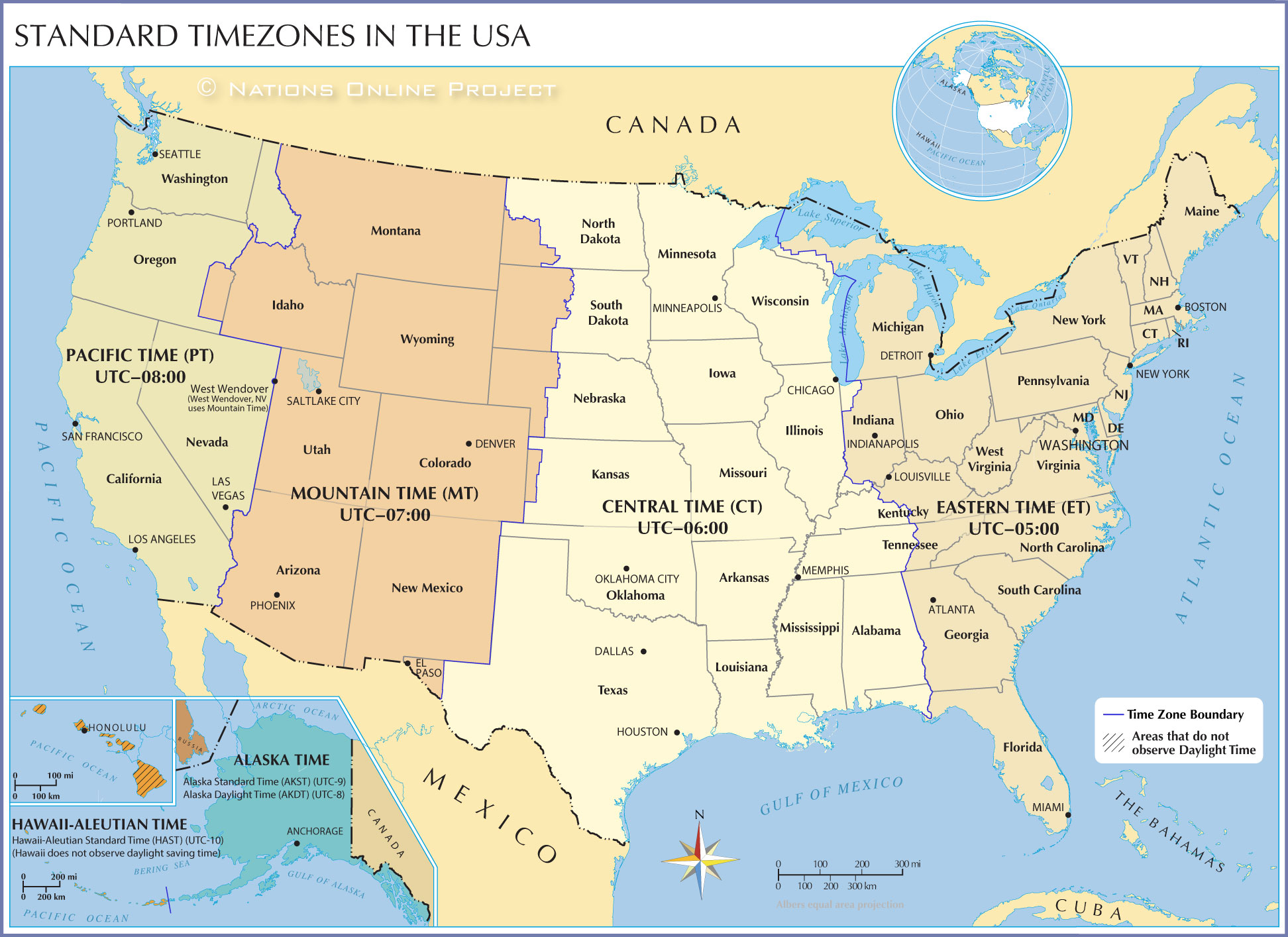
At its core, Pacific Standard Time is one of America’s six primary time zones, observed from early November to early March—aligning with the winter months when daylight saving time is no longer observed. Set at UTC−8 hours, PST dictates daily life across the West Coast: from the bustling urban core of Los Angeles to the tech hubs of Seattle and Vancouver (which observes PST despite being outside U.S.
borders). The time zone spans approximately 370,000 square kilometers, influencing not just business hours but cultural rituals like dinner gatherings, school start times, and public transit schedules. “PST isn’t just a clock—it’s a rhythm that shapes how millions begin and end their days,” notes Dr.
Elena Marquez, a sociologist at Stanford University studying regional time production.
Understanding Pacific Standard Time: Geography and Governance
The designation of Pacific Standard Time emerges from a blend of geographic necessity and federal regulation. Encompassing coastal regions from northern California to British Columbia, PST was officially adopted to standardize timekeeping across a Pacific-facing network of states, including California, Oregon, Washington, and parts of Nevada and Arizona—though Arizona observes Mountain Standard Time year-round due to its desert climate and legislative choice. The U.S.
time zones were formalized nationwide in 1883 by railroad companies seeking coordinated schedules, later codified by the Uniform Time Act of 1966.
Unlike some regions in neighboring countries that shift time based on daylight patterns, U.S. time zones—including PST—are fixed by statute. The decision to remain on PST year-round, unlike Arizona’s opt-in to daylight time, reflects enduring infrastructure design and seasonal planning.
“This consistency minimizes confusion for telecommunications, air travel, and cross-border commerce,” explains time policy analyst Marcus Reed. “PST anchors a system built on predictability.”
Daily Life and Practical Implications of PST
For residents, Pacific Standard Time imposes sharp rhythms. A morning routine in San Francisco begins earlier than in Phoenix—sunrise in LA may arrive at 5:45 AM local time, yet Pacific Standard Time standardizes that moment nationally, facilitating nationwide video conferences, stock trades, and emergency protocols.
Commuters trust PST to synchronize school buses, train departures, and worship services across towns miles apart.
In tech-centric regions like Silicon Valley, the precision of PST matters profoundly. Engineers schedule global stand-ups, developers sync codebases, and customer support teams rely on a shared window to respond. “Every notification, call, and collaboration hinges on this unchanging time,” states Sarah Lin, a project manager at a major tech firm in Oakland.
“PST isn’t just a timezone—it’s a digital infrastructure cornerstone.”



Related Post

Sevda Ela’s Net Worth Finally Revealed: The Rising Star’s Financial Snapshot Unveiled

Kentucky’s Time Zone Peculiarity: How Central Time Defines Life in the Bluegrass State

Lester Holt’s Stats Revealed: Age, Height, and the Icon Behind the Newsbench

Johny Johny Papa Yes: The Anthem That Cracked India’s Hearts and Sparked a Generational Shift

