Lewis Dot For F: Unlocking Atomic Speculation with Simplicity and Science
Lewis Dot For F: Unlocking Atomic Speculation with Simplicity and Science
In the intricate world of chemistry, where subatomic particles dictate the behavior of elements, the Lewis dot structure remains a foundational tool for visualizing valence electrons and predicting molecular bonding. Among these, the Lewis dot representation for fluorine—symbolized as F—offers a precise yet elegant snapshot of its electron configuration and chemical identity. Fluorine, the most electronegative element on the periodic table, exhibits unique reactivity and atomic character, making its Lewis dot structure not just a drawing, but a gateway to understanding its role in everything from biological processes to industrial chemistry.
The Basin of Electrons: Building the Lewis Dot Structure for Fluorine
Atom F, with atomic number 9 and a single valence electron, constructs its Lewis dot structure through a deliberate orchestration of dots around a central fluorine nucleus.
The atomic number guides this precision: fluorine possesses nine protons and nine electrons, and only one electron occupies its outermost shell. To reflect this, the structure displays a single filled dot on one side of the element symbol, visually anchoring its status as a halogen with a limited capacity to gain an electron and achieve stability.
The Lewis dot formula for fluorine is compact but deliberate: F· …this microdot denotes a single valence electron, emphasizing fluorine’s need for just one additional electron to complete a stable octet. Unlike elements that share electrons through covalent bonds, fluorine’s lone electron defines its reactivity—tendency to attract and bind strongly to electropositive atoms.
Similar to a lone key waiting for the right lock, the unpaired dot signals fluorine’s exceptional electronegativity and chemical dominance in compounds.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Significance of Fluorine’s Dot Arrangement
Fluorine’s electron configuration — 1s² 2s² 2p⁵ — reveals why its Lewis dot structure is so telling. With seven outer-shell electrons short of a full octet, fluorine’s意愿 (wèil(yīng, “wish” in classical rendering) to bond arises directly from the single empty p-orbital. This structural calling power manifests when fluorine shares its lone dot in a covalent link, as seen in F₂ molecules or fluorine’s bonds in NaF.
The structure thus acts not merely as a diagram but as a predictive model: the presence of one valence electron is the linchpin of fluorine’s identity and reactivity.
The spatial arrangement of fluorine’s lone dot — though non-bonding — exerts profound influence. In molecular systems, this dot becomes the site of electron donation, driving fluorine’s ability to stabilize nearby cations. For example, in hydrofluoric acid (HF), the lone electron on fluorine polarizes the bond, enabling hydrogen fluoride’s unique solubility and high dielectric constant.
In reaction mechanisms, the dot’s placement helps chemists anticipate how fluorine may initiate or participate in electron transfer processes, critical in catalytic cycles and bioinorganic systems.
Fluorine’s Lone Electron: Why It Matters in Bonding and Reactivity
While many elements form bonds through electron sharing or transfer, fluorine’s chemistry is anchored in its singular electron. Lewis dot theory clarifies why fluorine rarely forms ions compared to other halogens: its single valence dot is both a target and a frontier — easily donated, yet requiring investment. This dynamic explains fluorine’s status as a “bonding catalyst” in compounds like fluorocarbons, where resonance and electron withdrawal amplify stability through inductive effects.
In molecular orbital terms, fluorine’s unpaired electron contributes to anisotropic electron density, shaping molecular dipoles and reactivity profiles.
For instance, in combination with hydrogen, the dot’s influence helps define HF’s extreme acidity and strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding — phenomena absent in non-fluorinated analogs. Likewise, in fluorinated pharmaceuticals, the dot’s positioning guides molecular docking with biological targets, underscoring fluorine’s pivotal role in drug design and material science.
Key characteristics of the Lewis dot structure for F include:
- One solitary valence electron represented by a small icon (•) outside the atomic symbol
- No formal bonds—fluorine’s octet is temporarily incomplete
- Clear representation of electronegativity differences in bond polarity
- Visual cue emphasizing reactivity via the lone electron’s availability
Educational and Practical Applications of Fluorine’s Dot Pattern
Understanding the Lewis dot structure for fluorine is foundational not only for chemists but also for educators and students seeking to demystify periodic trends and molecular behavior. It exemplifies core principles: electron counting, octet rule adherence, and bonding drives by vacant orbitals.
In classrooms, drawing F’s dot structure reinforces core concepts, bridging theory and visualization.
Professionally, this structure supports predictive modeling in synthetic chemistry. By mapping fluorine’s valence electron, researchers anticipate reaction outcomes, design fluorinated reagents, and engineer molecules with enhanced stability or specificity. In industrial settings, such models guide the production of fluoropolymers, refrigerants, and pharmaceuticals—applications where fluorine’s unique dot pattern translates into tangible performance advantages.
In essence, the Lewis dot representation of fluorine—simple in form but profound in implication—unlocks a window into the subtle dance of electrons that governs chemical behavior.
From biological enzymatic sites to cutting-edge material synthesis, this microstructure underpins a macro-scale impact, proving that in chemistry, even the smallest dots carry enormous power.




Related Post
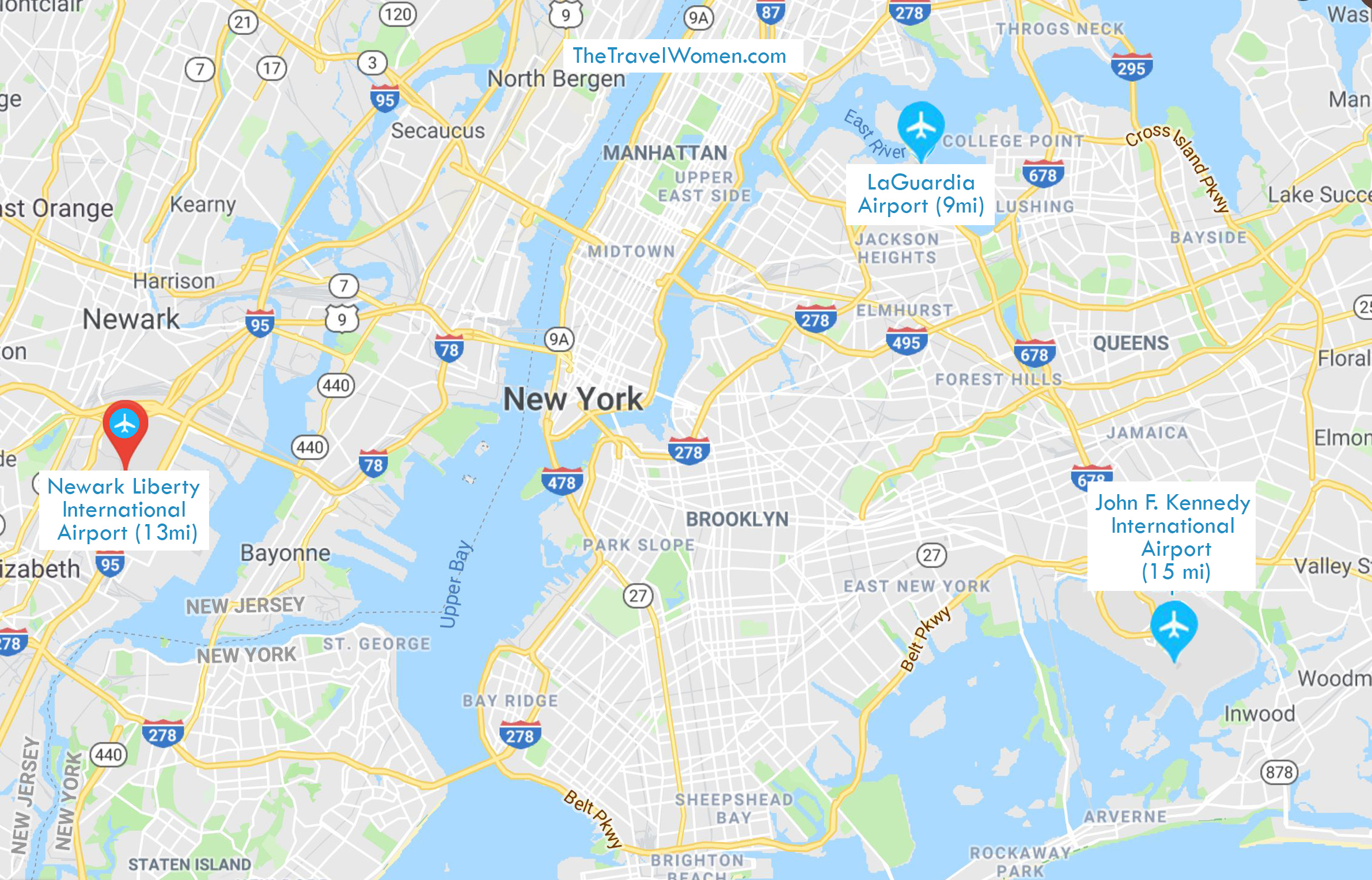
StatPenn Station to Newark Airport: The Fastest Gateway Between Manhattan and America’s Busiest Air Hub

Estate Sales Abilene Heating Up—Fast-Moving Fast-Sale Events Begin September 8, 2025

Joe Rogan’s Fire on the Frontlines: How Microdosing and Conscious Experimentation Are Reshaping Modern Wellness

Boca Juniors vs Benfica: A Clash of Cultures and Competitive Fire in a Global Showdown