HBr’s Lewis Structure Revealed: The Polar Bond That Drives Hydrobromic Acid’s Unique Chemistry
HBr’s Lewis Structure Revealed: The Polar Bond That Drives Hydrobromic Acid’s Unique Chemistry
The Atomic Arrangement Behind HBr’s Bonding Prowess
Hydrobromic acid (HBr) combines a proton and a bromine atom in a simple yet dynamically active structure, where bond polarity defines its reactivity
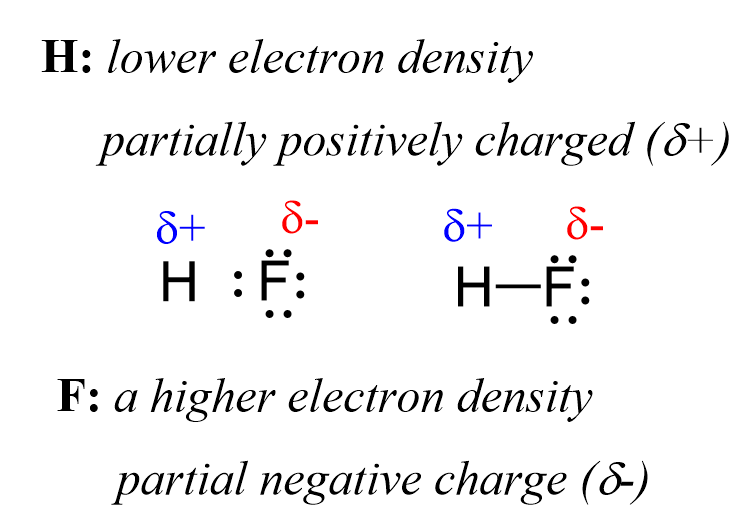
At the atomic level, the Lewis structure of hydrobromic acid reveals a single hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a bromine atom, forming a polar covalent molecule. Though HBr is often represented as a diatomic unit, real chemical behavior arises from the electronegativity disparity between hydrogen (EN ≈ 2.20) and bromine (EN ≈ 2.96). With bromine significantly more electronegative, the shared electron pair is drawn closer to the bromine atom, generating a dipole moment that gives HBr its characteristic polarity.
This polarity is not merely an academic detail—it directly influences the compound’s acid strength, solubility, and interactions in both biological and industrial systems.
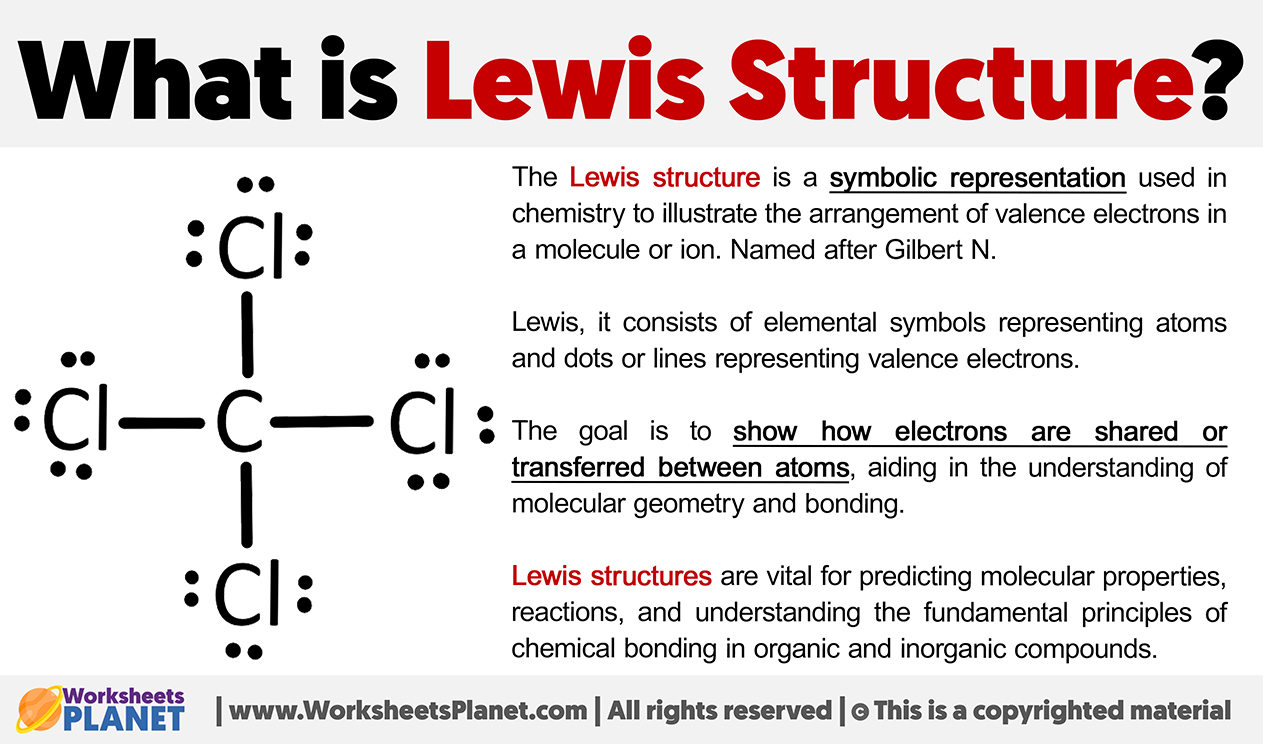
The Lewis structure shows HBr as a linear molecule with a single bond—electron counts confirm 8 valence electrons around bromine (outer-day principle) and 2 around hydrogen (a duet). Despite the short length of the molecule, the unequal electron distribution is the cornerstone of its chemical behavior. Unlike nonpolar molecules such as H₂O or O₂, HBr’s uneven charge distribution enables it to readily donate protons in aqueous solutions, making it a strong acid with a low pKa (~−9), among the strongest hydrous acids.
Electron Distribution and Polarity in HBr’s Molecular Framework
Broken down into atomic terms, the Lewis structure emphasizes electron density asymmetry.
Bromine, with its larger atomic radius and higher electron-gathering tendency, occupies the bulk of the shared electron cloud. This creates a visual and electrostatic gradient: a partial positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen and a partial negative charge (δ−) on bromine. “The bond polarity directly governs HBr’s ability to act as a proton donor,” notes Dr.
Elena Vasquez, a physical chemist specializing in acid-base systems. “Without this electronegativity-driven dipole, HBr would lack the strength and reactivity that define its utility in chemistry.”
The bond angle in the isolated HBr molecule is effectively 180 degrees, a linear geometry typical of sp hybridization in binary molecules. However, in solution, HBr exists primarily as a dimer—H₂Br—held together by weak intermolecular halogen bonds rather than covalent connectivity, though each H–Br bond retains its polar character.
This structural adaptability underscores the molecule’s resilience in diverse chemical environments, from concentrated acids to aqueous media.
From Molecular Geometry to Acid Strength: The Functional Impact of HBr’s Structure
The distribution of electron density in HBr has profound practical consequences. Its strong acidity arises because the polar bond lowers the activation energy for proton dissociation:
- “The good leaving group character of Br⁻, combined with the highly polarized Br–H bond, makes HBr an efficient acid,” explains Dr. Vasquez.
“The energy released when H⁺ separates is substantial—this explains its dominance over other hydrogen halides in strong acid behavior.”
- HBr dissolves readily in water to generate hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) and bromide (Br⁻), a process facilitated by the molecule’s polarity and the solvation power of water.
- Its hydrogen-bonding capacity enhances solubility in polar solvents, a trait exploited in chemical synthesis, industrial reaction media, and biological transport mechanisms.
- Despite being a gas at room temperature, HBr vaporizes easily due to weak intermolecular forces, confirming the dominance of covalent over van der Waals interactions in its molecular integrity.
Unlike covalent molecules that decompose under mild conditions, HBr maintains structural coherence in solution until proton transfer occurs—a stability anchored in bond polarity.
Safety, Handling, and Real-World Implications of HBr’s Bonding
Understanding HBr’s Lewis structure is not just academically satisfying—it is essential for safe handling and industrial application. The molecule’s polarity contributes to its corrosive and toxic nature. As a strong acid, it generates significant heat upon dilution and reacts violently with silver or alkaline metals, posing direct hazards in labs and plants.
“Professionals working with HBr must prioritize protection against both its chemical aggressiveness and the exothermic nature of its proton release,” warns industrial chemist Mark Reynolds. “The polar bond is at the root of these risks—its electronegativity-driven charge separation fuels reactivity.”
In environmental contexts, HBr’s behavior reflects broader trends among hydrogen halides: its volatility and solubility influence atmospheric chemistry, acid rain formation, and aerosol dynamics. Controlled generation and neutralization of HBr remain critical in semiconductor etching, pharmaceutical synthesis, and analytical chemistry—processes that depend fundamentally on predictable bonding and reactivity patterns rooted in molecular structure.
The Enduring Significance of HBr’s Lewis Structure in Modern Chemistry
At its core, the Lewis structure of hydrobromic acid illuminates how a simple polar covalent bond can drive extraordinary chemical behavior.
From electron distribution to acid strength, solubility to safety considerations, the molecule’s behavior emerges predictably from its atomic configuration. Recognizing HBr not as a static diatomic duo but as a dynamic, polar entity enriches our understanding of acid-base chemistry across scientific and industrial frontiers. As both a cornerstone of inorganic compounds and a gateway to complex electrochemical processes, HBr’s structure remains indispensable to modern chemistry—proving that even in simplicity, molecular design holds the key to profound reactivity and utility.

Related Post
Lee Ingleby: From Bluffing Charmer to Credible Screen Icon

What If Your Discord Server Could Talk? Add Custom Bots to Unlock Unmatched Power

Understanding The Gypsy Rose Crime Photo: A Deep Dive Into The Controversy and Investigation

Explorando El Universo De Goku: Un Vistazo Profundo A Sus Personajes En Dibujo

