Find The Volume Of The Prism Iready
Find The Volume Of The Prism Iready: Mastering 3D Volume Calculations The geometric world unfolds through precise measurements and calculations, and few concepts are as fundamental in engineering, architecture, and design as the volume of a prism. When learning to determine volume using tools like “Find The Volume Of The Prism Iready,” an organized, step-by-step approach transforms abstract formulas into tangible results. This guide uncovers the essentials, from definitions and formulas to practical applications—empowering students, educators, and professionals to tackle prism volume with clarity and confidence.
At the core of any prism lies a simple but powerful structure: two parallel, congruent bases connected by rectangular lateral faces. The volume of a prism is defined as the product of its base area and height, expressed mathematically as
But beyond memorizing — finding the volume accurately demands understanding the underlying principles.
Paris-based engineer Marcus Delgado explains, “Every prism, regardless of shape, follows the same foundational logic. What varies is the base’s geometry—triangular, rectangular, or irregular—but the method remains unified.” This consistency makes volume determination both predictable and scalable, whether analyzing a water tank or architectural modeling.One of the most common realizations when learning prism volumes is recognizing that real-world applications often require converting irregular shapes into measurable base areas.
For simple prisms—such as rectangular bases—a direct measurement suffices. If a prism’s base measures 8 cm by 5 cm, the base area is 40 cm². Standing 10 cm tall, the volume becomes 40 × 10 = 400 cm³.
But when the base is triangular or hexagonal, the approach demands precision:- Triangular base: calculate area as
B = ½ × base × height - Hexagonal base: apply
B = 3√3 × s²⁄2 for regular hexagons, wheres is the side length - Irregular bases: use triangulation, dividing into regular shapes or apply coordinate geometry
Step-by-step: Calculating Prism Volume Explained
- Identify base type: Rectangular, triangular, or circular—each defines a unique area formula.
- Measure base dimensions: Precision is critical; use calipers or scaled drawings for accuracy.
- Compute base area: Apply the appropriate formula—recall that
B = A for base area andh for height, ensuring alignment of dimensions. - Multiply for volume: V = B × h. Pay close attention to units: a cm³ height with cm² base yields cm³ volume.
- Validate the result: Use estimation—approximate base area or height by rounding, then verify the calculated volume is reasonable. Calculators built around the
For example, a rectangular prism with length 6 m, width 4 m, and height 3 m generates:
“Students often struggle not because math is hard, but because they don’t visualize the 3D structure,” notes Dr. Elena Torres, STEM curriculum developer. “Tools that overlay virtual bases on sketches bridge that gap.” The “Find The Volume Of The Prism Iready” system supports this by rendering 3D models that highlight the base and height dimensions in real time.
In professional contexts, accurate volume calculations safeguard structural integrity and cost efficiency. Architects rely on precise prism measurements to estimate material quantities, while logistics teams use volume data for shipping container optimization. In construction estimates, a 1% error in volume can translate to hundreds of dollars in over- or under-buying concrete, lumber, or insulation. Reliable calculations, therefore, are not just academic—they drive real-world savings and safety.
Mathematically, while the formula remains constant, complexity increases with non-uniform cross-sections.Prisms with curved bases—such as a conical frustum—are not true prisms (they lack parallel, congruent bases), but analogous forms like the prismoid still use integrated area averages. Still, for strict prism definitions, rectangular prisms remain the cornerstone of learning.
Technology platforms now integrate augmented reality (AR) to visualize volume in context—projecting a prism with highlighted base and height dimensions, dynamically scaling with user-inputted measurements. This fusion of geometry and interactivity transforms passive learning into active exploration.As one “Find The Volume Of The Prism Iready” user described, “Seeing the base area expand in AR while hearing it multiply by height makes abstract math feel real.” Mastering prism volume is more than a classroom exercise—it’s a gateway to understanding spatial relationships, material efficiency, and structural logic. The
With clarity, tools, and practice, every prism yields its volume—not just as a number, but as a measurable truth in the language of design.




Related Post

Where Is Poland On The World Map? Precision, Place, and Global Positioning Explained
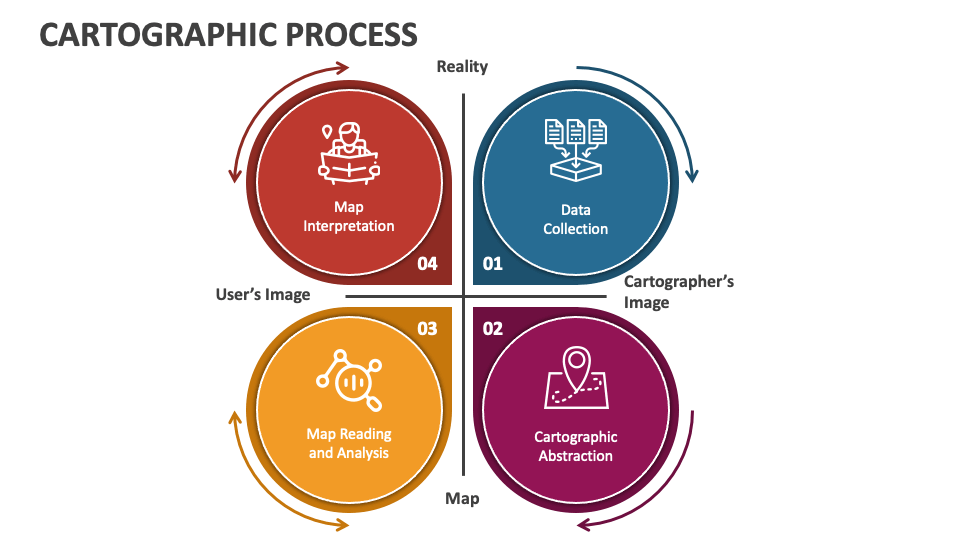
On Map: Precision, Purpose, and Process in Modern Cartographic Navigation

Skipthegamesocala: Unseen Insights Into a Hidden Gem of Competitive Gaming
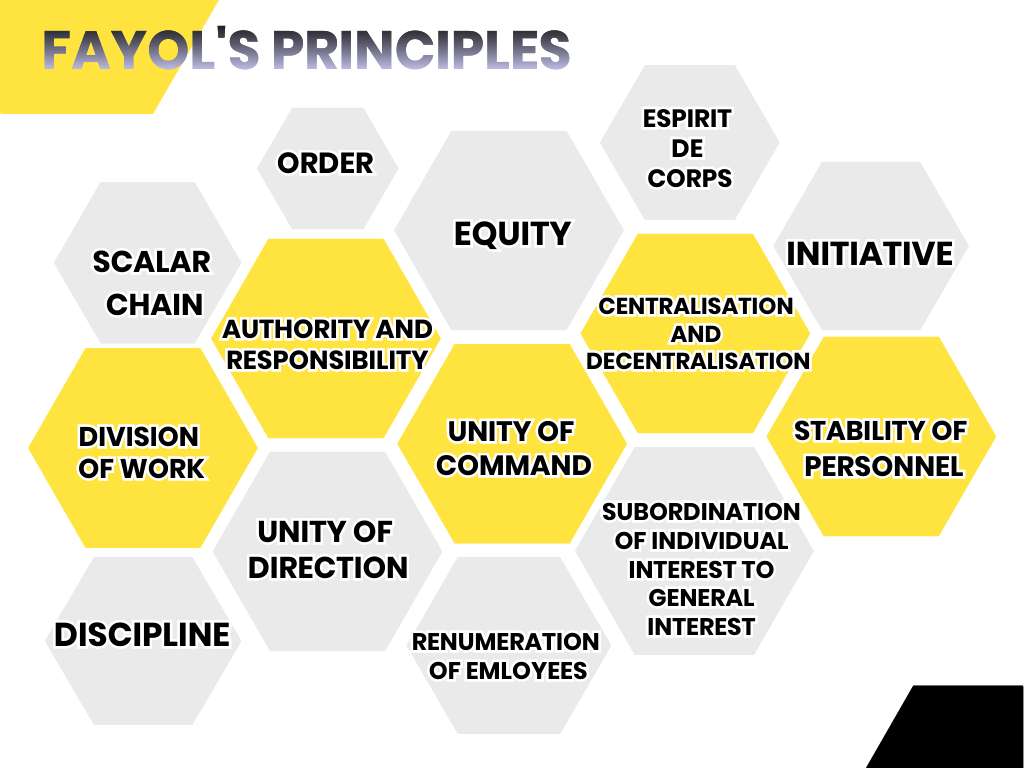
Fayol’s Timeless Management Principles: The Blueprint for Business Growth That Still Delivers Today

