Command-Based Interface: The Power of Simplicity in Command-Line Mastery
Command-Based Interface: The Power of Simplicity in Command-Line Mastery
Command-Based Interface (CBI) has transformed how users interact with complex systems—delivering precision, efficiency, and control through text-based commands. Far from outdated, CBI remains a cornerstone of productivity for developers, system administrators, and tech enthusiasts who value direct, unmediated access. This article explores how CBI functions, its core advantages, practical applications across industries, and why mastering command interfaces is no longer optional—but essential.
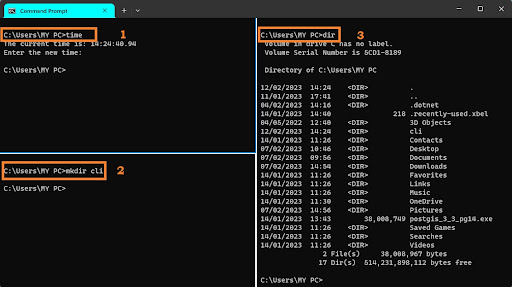
At its core, a Command-Based Interface enables users to execute tasks via plain text commands entered through a terminal or shell environment.
Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs), which rely on mouse clicks and visual menus, CBI emphasizes operational clarity and consistency. Every command is a statement: a precise instruction decoded and executed by the system. “Commands are structured, repeatable, and carry explicit meaning,” explains Dr.
Elena Torres, a computational linguist at the Institute for Human-Computer Interaction. “This precision reduces cognitive load and accelerates task completion.” By stripping away visual clutter, CBI empowers users to focus on what matters—operations.
Core Components of a Command-Based Interface
A functional Command-Based Interface integrates several key components that define its usability and power:
- Command Syntax: Each command follows a standardized format—usually a verb followed by an object (e.g., `git commit -m "message"`)—ensuring consistency and predictability. Early Unix systems pioneered this convention, and it remains foundational today.
- Standardized Output: Commands return structured text or data in predictable formats (like JSON or plain text), enabling programmatic integration and automation.
- Parameterization: Users extend commands with optional flags and arguments, such as `sudo chmod 755 file.txt`, allowing granular control over system behavior.
- History and Auto-Recall: Most CBI environments support command history via keys like `Ctrl+R`, enabling rapid access to past actions without rekeying.
- Shell Scripting: The ability to sequence commands into scripts lets users automate workflows, from backups to server monitoring, reducing manual effort exponentially.
These features combine to form an ecosystem where simplicity and sophistication coexist—a paradox that makes CBI both accessible to beginners and indispensable to experts.
Industry-Wide Adoption and Real-World Impact
Command-Based Interfaces are not confined to niche technical circles. Across industries, they drive efficiency, security, and scalability. In software development, Git’s command-driven model underpins version control, enabling distributed teams to collaborate seamlessly.
System administrators rely on Bash, PowerShell, and CLI tools like `rsync` and `awk` to manage servers at scale. “No longer restricted to night shifts,” notes Mark Chen, cloud engineer at TechCore Solutions, “modern CI/CD pipelines are orchestrated through CBI workflows that are faster, more transparent, and easier to audit.”
In critical infrastructure, CBI ensures operational resilience:
- Server Administration: Tools like `ssh`, `ps`, and `systemctl` let operators diagnose and reboot systems remotely with a single command.
- Data Engineering: Scripts using `grep`, `sed`, and `curl` automate data pipeline transformations, reducing errors and latency.
- Cybersecurity: Shell-based monitoring tools analyze logs in real-time, detecting anomalies faster than GUI dashboards in many cases.
Even in emerging fields like AI model deployment, cloud platforms such as AWS and GCP provide CLI interfaces for batch processing and model training—proving C


Related Post
Is Keith Mc Gillvery Married? Unveiling the Personal Life of a Public Figure Under Scrutiny

Unlocking Precision in Structural Characterization: The Critical Role of IsCC in Modern Chemistry

Ubnbound Escape Cube Pokemon

Unlocking Enterprise Insights: How Saberspark Age Transformed Data Processing

