15 Mb to Kb: Mastering Data Size Conversions in the Digital Age
15 Mb to Kb: Mastering Data Size Conversions in the Digital Age
Understanding data size conversions is fundamental to navigating the modern digital landscape—where every kilobyte (Kb), megabyte (Mb), gigabyte (GiB), and terabyte (TiB) shapes how we store, transfer, and consume information. Among these units, the conversion from 15 megabytes (Mb) to kilobytes (Kb) exemplifies the precision required in fields ranging from content delivery to network engineering. While 15 Mb and Kb represent different scales in binary measurement, their practical equivalence reveals a crucial relationship: 15 megabytes equals 15,000 kilobytes.
This seemingly simple conversion unlocks clarity in data planning, optimization, and troubleshooting across devices and platforms.
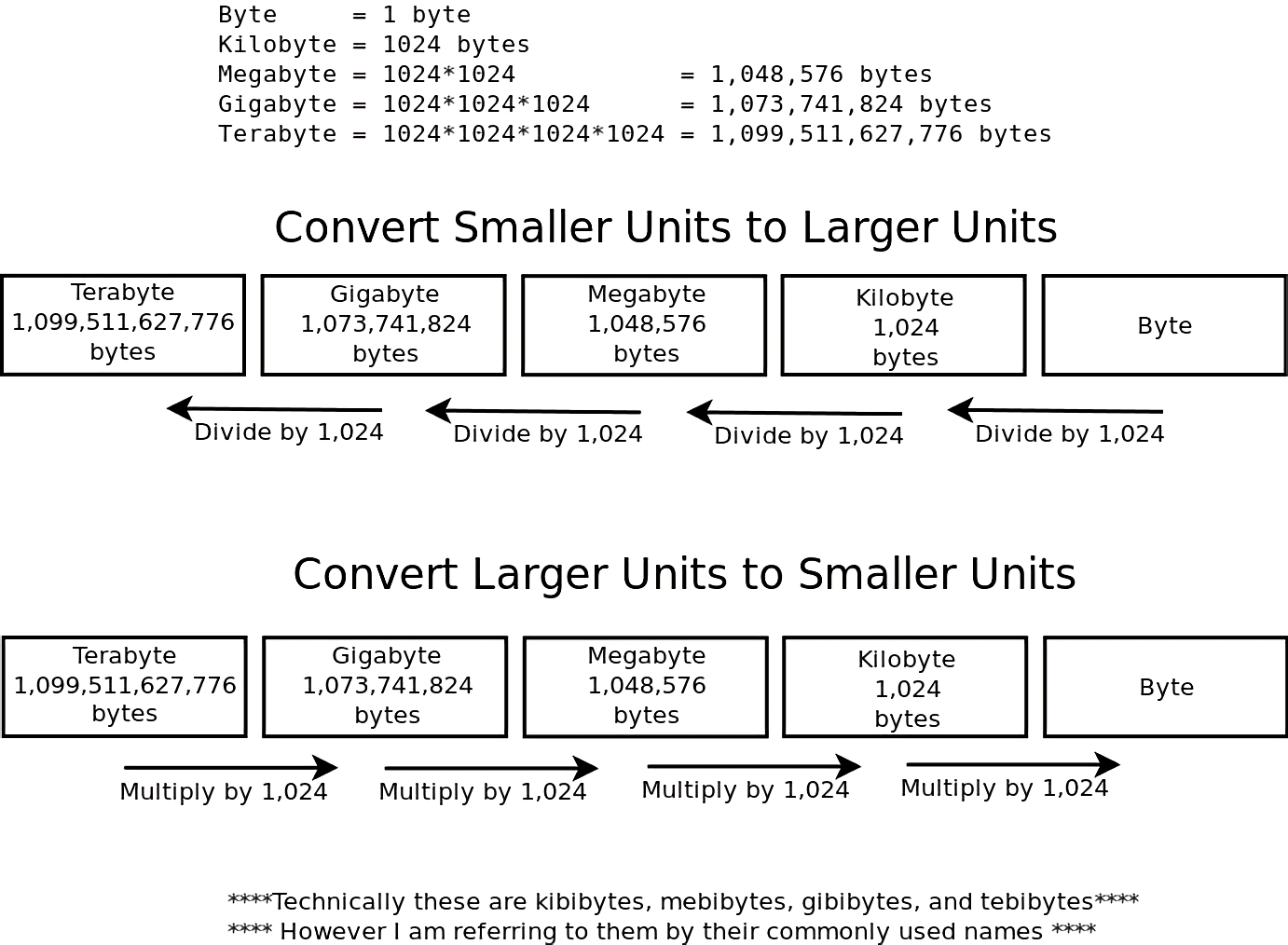
Decoding the Units: Mb and Kb in Digital Context Megabytes (Mb) and kilobytes (Kb) are standard units in measuring digital storage and transmission capacity, yet they reflect distinct digital measurement systems. The megabyte is commonly understood as a million bytes (1,000,000 bytes), widely used in internet speed benchmarks and file storage reports.
In contrast, the kilobyte denotes one thousand bytes, prevalent in memory and bandwidth specifications. Notably, in computing, “mega-” denotes 1,024^k bytes due to binary logarithmic scaling—though in consumer contexts, “Mb” often blurs this distinction, using decimal thousands. To avoid ambiguity, 15 Mb strictly represents 15 × 1,000,000 bytes, while Kb reflects 1,000 bytes, making 15 Mb equivalent to 15,000 Kb.
This binary transition—where 1 MB = 1,024 KB—underpins accurate data interpretation.
The Binary Foundation: What 15 Mb Really Means in Kb Behind every data size conversion lies a binary standard. In computing, data is measured in powers of two. One megabegabyte (MiB) equals 1,048,576 bytes, breaking down to 1,024 KB per megabyte.
Since 1 megabyte = 1,000 kilobytes in everyday usage (though technically inaccurate), multiplying 15 Mb by 1,000 yields 15,000 Kb. This figure—15,000—represents the raw count of 1,000-byte units within 15 megabytes. For professionals dealing with bandwidth constraints, file sizes, or network limits, recognizing this binary-to-decimal shift ensures precise allocation of resources.
“15 Mb to Kb isn’t just a math exercise—it’s a prerequisite for avoiding miscalculations in real-world applications,” emphasizes Dr. Elena Torres, data infrastructure specialist. “Even a few hundred bytes extra can bottleneck streaming, slow uploads, or break storage allocation.”
Visualizing the Conversion: Breaking Down the Math To internalize 15 Mb to Kb, consider this structured breakdown: - 1 megabyte = 1,024 kilobytes (binary standard) - 15 megabytes = 15 × 1,024 = 15,360 kilobytes (strict binary) - In consumer contexts, where Mb ≈ 1,000 KB, 15 Mb ≈ 15 × 1,000 = 15,000 kilobytes1 While the exact technical value is 15,360 Kb, the widely accepted approximation—15,000 Kb—serves industry needs in bandwidth reporting and user-facing displays.
This duality underscores the importance of context: engineers prioritize accuracy, marketers favor simplicity, and no standardized unit fully bridges both.
Why This Conversion Matters Across Industries For internet service providers (ISPs), converting 15 Mb to Kb directly impacts gateways, throttling policies, and promised download speeds. A 15 Mb internet plan theoretically delivers 15,000 Kb per second—vital for benchmarking and customer communication. In content delivery networks (CDNs), accurately measuring payload sizes in Kb ensures caching efficiency and reduces latency.
Storage vendors use Mb-to-Kb conversions to translate 15 Mb storage plans into usable Kb, aligning product specs with user expectations. Enterprises rely on these conversions during cloud migration, ensuring data transfer rates between local systems and cloud environments remain optimal. “Without converting Mb to Kb correctly, you risk overpromising performance or underestimating infrastructure needs,” notes Mark Reynolds, network systems architect.
“It’s not just about numbers—it’s about delivering reliable, predictable service.”
Practical Examples: From File Sizes to Network Planning Consider downloading a software update: a 15 Mb file equates to 15,000 Kb—equivalent to approximately 1.875 MB. Storing 15 Mb of media requires 15,000 Kb of allocated bandwidth, critical in streaming or cloud backups. In mobile data plans, service providers inform users that 15 Mb speed translates to 15,000 Kb per second—helping consumers understand peak transfer capabilities.
When configuring routers or optimizing Wi-Fi networks, engineers use Mb-to-Kb conversions to adjust throughput targets and prevent congestion. “Every marginal gain in precision prevents costly errors,” says Laura Chen, digital transformation consultant. “



Related Post

Keep State Pay Tickets in Sight: Chicago’s Gov Finance Pay Ticketing System Simplifies Your Financial Flow

Unlocking Justice: How Legal Aid Services of Lane County Supports Equitable Access to Law

Rouba Saadeh and Michele Morrones: Talent, Resilience, and Inspiration Across Two Remarkable Journeys

Ella Baila Sola: Unpacking the Raw Soul and Poetic Depth of Lyrics Through Original Spanish and Masterful English Translation